Guaranteed Performance For
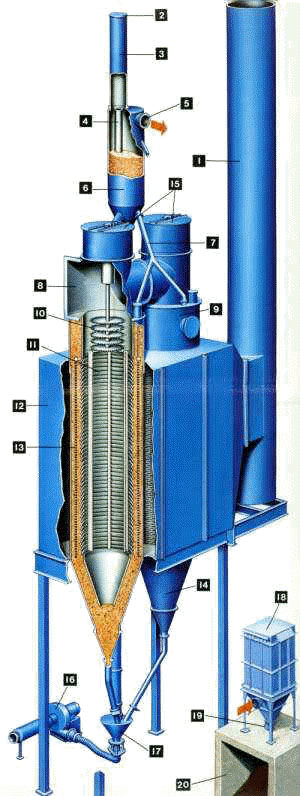
The Electrified Filter Bed (EFB®), developed by EFB, Inc. is a unique air pollution control system for the removal of fine particulate matter and condensable hydrocarbons from industrial exhaust gases. After being ionized, pollutant is separated from the gas stream and deposited electrostatically on the surface of pea-sized gravel. This results in high filtration efficiency unmatched by other devices.

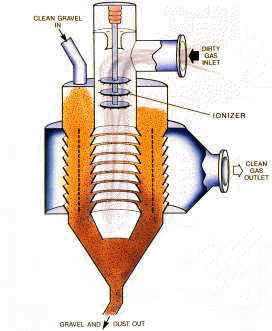

The Ionizer electrostatically charges dust and aerosols in the inlet gas stream. Spiked metal disc electrodes are hung concentrically within a circular electrically grounded entrance duct. These electrodes are held at a high negative DC voltage which causes a Corona Discharge to form at the tip of each spike. The electrical ions formed by the corona are deposited onto the passing particulates. This highly effective process electrically charges the particulates to near saturation levels.
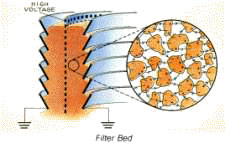
Dust and aerosols are removed from the gas stream in the electrostatic Filter Bed. The bed consists of pea sizes natural gravel held between wide slats of metal called louvers. A perforated High Voltage Electrode in the bed electrically polarizes the stones, inducing alternate caps of positive and negative charge on them. Negatively charged particulates are attracted and attached to the positive caps. The EFB achieves high filtration efficiency by virtue of the immense electrostatic collection surface available in the granular bed.
The gravel in the filter is continuously cleaned and recycled. As the gravel moves, dust is retained in it by EFB?s patented method called "Electromechanical Freezing". The high voltage electrode provides an intense electrical field which makes the dielectric stones and dust attract each other, much like iron filings do in a magnetic field. As a result, the gravel moves downward as a "frozen" plug, retaining collected dust with high efficiency.

The EFB was developed specifically for the removal of fine particulate matter and condensable hydrocarbons form industrial exhaust gas streams. Dust and aerosols are ionized and then deposited onto the surface of pea-size gravel by electrostatic forces. Some advantages of the EFB system are:
Submicron Particulate
Electrostatic collection onto the tremendous amount of surface provided by the granular filter media results in high collection efficiencies, especially for submicron particulates.
Blue Haze
The EFB captures submicron hydrocarbon aerosols, eliminating opacity and "blue haze".
Fire Resistance
The filter medium is gravel. This makes the unit inherently resistant to fire damage.
"Sticky" Pollutants
Pollutant is cleaned from gravel in external systems. This allows effective operation with the sticky pollutants typical of hydrocarbon fumes.
Totally Dry
Pollutant is captured in its original dry form, no sludges or slurries are involved Equipment is not subject to corrosion,
Low Power
Because of the two stage electrostatic collection process, electrical power for the high voltage is negligible.
Easy Installation
Equipment is small, especially the floor space required, allowing easy retrofit into existing plants and low installation costs.
Durable Equipment
Simple rugged components result in trouble-free operation. Use of gravel filter media allows operation at elevated temperatures.
After collection of particulate matter in the gravel bed, the gravel is continuously cleaned in a pneumatic system developed specifically for the EFB system. At the same time the cleaned gravel is transported to the top of the system to be used again in the filter.
Collected dust is conveyed in dry, low pressure, low temperature air to a silo or bunker equipped with a small dust collector. This can be located practically anywhere in the plant, usually where other waste materials are deposited. No other conveying systems are needed.